News
Passion, dedication, innovation, enterprising, integrity, truth-seeking, altruism, win-win

Passion, dedication, innovation, enterprising, integrity, truth-seeking, altruism, win-win

Do you worry about system failures in high-pressure environments? Inferior piping leads to costly downtime and safety risks. Our precision tubing ensures your projects run flawlessly every time. Small diameter stainless steel tubing is a precision-engineered hollow component, typically under 25.4mm OD, designed for critical applications like medical devices and aerospace hydraulics. It offers superior corrosion resistance, high strength-to-weight ratios, and tight tolerances, making it the backbone of modern, high-performance industrial systems.

You might think all tubes are the same, but the difference lies in the details. Let me show you exactly why quality matters.
Finding versatile materials for complex projects is frustrating. You need a solution that adapts to medical, aerospace, and industrial needs without compromising safety. The widespread utility of these tubes comes from their ability to maintain integrity in harsh conditions. They are vital for medical sterility, aerospace weight reduction, and precise chemical flow control, proving indispensable where failure is not an option.
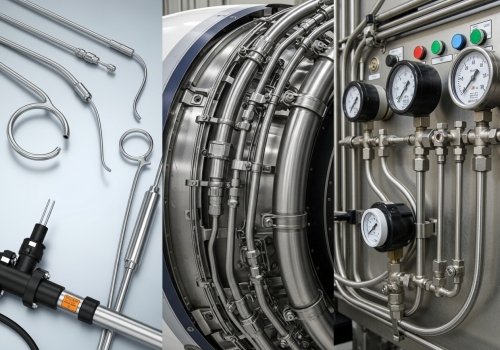
I have spent years at Centerway Steel watching how these components drive innovation across sectors. When we talk about small diameter stainless steel tubing, we are not just talking about pipes; we are talking about the arteries of modern industry. Let me break down exactly where these materials shine, based on my experience supplying global partners.
In the medical field, there is no room for error. We supply 316L grade tubing for catheters, endoscopes, and surgical tools because it is biocompatible. It withstands repeated sterilization cycles without corroding. I always tell my clients that if a material cannot handle the autoclave, it does not belong in a hospital.
Weight is the enemy of flight. Aerospace engineers love these tubes for hydraulic lines and fuel delivery systems because they have an incredible strength-to-weight ratio. They handle the vibration of a jet engine and the pressure of a hydraulic lift simultaneously.
In the oil and gas EPC projects I work with, accurate data is everything. These tubes connect pressure gauges and flow meters. Their smooth internal bore ensures that the fluid flows evenly, giving accurate readings. A rough tube means bad data, and bad data leads to bad decisions.
This is about purity. In chip manufacturing, even a microscopic particle can ruin a batch. We provide electropolished tubing that is so smooth inside that contaminants have nowhere to hide. This maintains the vacuum integrity needed for high-tech production.
Selecting the wrong alloy leads to rapid corrosion and structural failure. This mistake wastes budget and endangers your entire operation's integrity. The right grade depends entirely on your specific environment. While 304 is the industry workhorse for general fluids, 316L offers superior marine corrosion resistance, and specialty grades like 321 handle extreme heat effectively.
At Centerway Steel, I often see purchasing managers struggle to balance cost with performance. It is crucial to understand that not all steel is created equal. The chemical composition determines whether a tube lasts twenty years or leaks after six months. Here is how I break down the material selection for my clients to ensure they get exactly what they need.
I have compiled a table below to help you visualize the differences. This is based on the requests we process daily.
| Grade | Key Elements | Why Choose It? | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 / 304L | 18% Chromium, 8% Nickel | It is the standard "workhorse." Excellent formability and decent corrosion resistance. 304L has low carbon to help with welding. | General fluid lines, lab equipment, architectural supports. |
| 316 / 316L | Added Molybdenum | The "Marine Grade." It resists salt and chlorides much better than 304. | Chemical processing, medical implants, marine environments. |
| 321 | Titanium Stabilized | It stands up to high heat (425-850°C) without losing its structure. | Aircraft exhaust, high-temp chemical lines. |
| 904L | High Nickel & Copper | A "Super-Austenitic" grade. It fights off strong acids like sulfuric acid. | Pollution control, harsh pulp and paper processing. |
Sometimes, even the best stainless steel is not enough. For extreme heat or aggressive chemical environments, I recommend looking at Nickel alloys like Inconel. While more expensive, they resist oxidation at temperatures where steel would fail. However, for 90% of applications, a correctly chosen small diameter stainless steel tubing grade is the most cost-effective and reliable choice.
Poor surface finish and weak welds cause contamination and leaks. These hidden defects destroy system efficiency and ruin sensitive production processes. The manufacturing method dictates the tube's pressure limit and cleanliness. Seamless tubes are essential for high-stress areas, while welded options offer economy. Understanding these distinctions ensures you specify the perfect tube for your unique technical requirements.
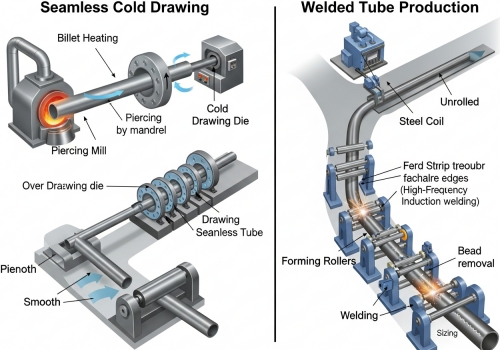
When I advise clients on specifications, I focus on the "how" as much as the "what." The way a tube is made changes its physical properties. You also need to distinguish between "small diameter" and "micro" tubing, as they serve very different masters.
· Seamless vs. Welded: Seamless tubes are drawn from a solid billet. They have no seam, meaning they have uniform strength all the way around. I recommend these for high-pressure safety. Welded tubes are rolled from a strip. They are cheaper and great for aesthetic or low-pressure uses.
· Cold Drawing: This process pulls the tube through a die to shrink it. It hardens the metal and makes the dimensions incredibly precise.
· Finishing: For my pharmaceutical clients, I suggest electropolishing. This chemical process strips away the outer layer of metal, leaving a mirror-like finish that bacteria cannot stick to.
It is important not to confuse these terms. Here is a quick comparison to help you categorize your needs.
| Feature | Small Diameter Tubing | Micro Stainless Tubing |
|---|---|---|
| Size Range | Typically 1mm to 25mm | Usually under 1mm |
| Primary Use | Fluid transfer, fuel lines, cooling loops | Hypodermic needles, precision sensors |
| Tolerance | Tight (±0.05 mm) | Extremely Tight (±0.005 mm) |
| Cost | Moderate | High (due to processing difficulty) |
Selecting the right tubing requires balancing material grade, manufacturing style, and application needs. At Centerway Steel, we ensure you get the precise, high-quality solution your project demands.